

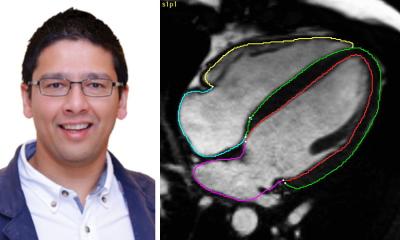
The potential of AI to predict mortality based on heart measurements highlights its potential to revolutionise cardiac care and improve patient prognosis
Hosamadin Assadi
While other studies have investigated the use of AI in interpreting MRI scans, this latest AI model was trained using data from multiple hospitals and different types of scanners, as well as conducting the testing on a diverse group of patients from a different hospital. In addition, this AI model provides a complete analysis of the entire heart using a view that shows all four chambers, while most earlier studies focused on a view that only looks at the heart’s two main chambers.
PhD student Dr Hosamadin Assadi, of UEA’s Norwich Medical School, said: “Automating the process of assessing heart function and structure will save time and resources and ensure consistent results for doctors. This innovation could lead to more efficient diagnoses, better treatment decisions, and ultimately, improved outcomes for patients with heart conditions. Moreover, the potential of AI to predict mortality based on heart measurements highlights its potential to revolutionise cardiac care and improve patient prognosis.”
The researchers say future studies should test the model using larger groups of patients from different hospitals, with various types of MRI scanners, and including other common diseases seen in medical practice to see if it works well in a broader range of real-world situations. Other recent research from the teams at UEA, Leeds and Sheffield has refined the method of using heart MRI scans for female patients, particularly for those with early or borderline heart disease, which meant that 16.5% more females were able to be diagnosed.
The research was a collaboration between the University of East Anglia, the University of Leeds, the University of Sheffield, Leiden University Medical Centre, the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust. The study was supported by funding for Dr Pankaj Garg from the Wellcome Trust Clinical Research Career Development Fellowship.
Source: University of East Anglia